Introduction of Virtualization?
Why Virtualization?
Most administrator will look to server virtualization to help reduce the physical footprint of their datacenter or infrastructure.
According to the analyst firm gartner, more than 70% of IT budgets are spend on infrastructure.
According to December 2007 Survey 60% of them were relying on VMware.
According to the analyst firm gartner, more than 70% of IT budgets are spend on infrastructure.
According to December 2007 Survey 60% of them were relying on VMware.
Power and utility companies also see the benefit from machine virtualization, since their customers can greatly reduce their power.Greenhouse gas or Greening the datacenter or Carbon footprint of datacenter.Greening the datacenter means more than just reducing the number of physical servers contained within it. It means moving forward with green policies and practices.
Moving to Virtualization relies on five key steps:-
1.Discovery
2.Virtualization
3.Hardware Maximization
4.Architecture
5.Management
Discovery
How can you move virtualization if you don’t know how many servers are running in network. It’s time to protect the system and application it run from disaster recovery. Easiest way to generate an inventory of your network is to work with free tool is Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer.VMware also offer two tool can be used for an assessment of the Server both
physical and virtualization. VMware guided consolidation CiRBA’s Data Center Intelligence (or) Plate Spin’s Power Recon Tool
Virtualization
Today virtualization technology has evolved and can now apply to multiple layers with in the datacenter.
Let me understand seven layer of virtualization.
SerV is focused on partitioning a physical Instance of an operating system into a
virtual instance or Virtual instance or Virtual machine.
i) Software Virtualization (Soft V)
Run the virtualized operating system on the top of a software virtualization platform running on an existing operating system.
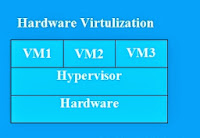
ii) Hardware Virtualization (Hard V)
Run the virtualized operating system on the top of a software virtualization platform
running on top of the hardware without an existing operating system. The engine used to run
hardware virtualization is usually referred to as hypervisor. To purpose of hypervisor to expose hardware resources to the virtualized operating system.
2.Storage Virtualization.
Store V is used to merge physical storage from multiple devices so that they appear as
one single storage pool. The Storage in this pool can take several forms; DAS, NAS or SAN and it
can be lined to through several protocol FC, iSCSI FC on Ethernet or even the
NFS. Storage virtualization is the ability to rely on thin provisioning or the assignation of a
logical unit (LUN) of storage of a given size.
3. Network Virtualization
Let you control available bandwidth by splitting it into in-depended channels that can
be assigned to specific resources.Network virtualization is the VLAN, Which creates
a logical segregation of a physical network. So that we can segregate VM as logical network
as into perimeter network, server network.
4. Management Virtualization
This technologies that manage the entire datacenter, both physical and virtual to present
one single interface for the provision of services.
i) Resource Pool
Which includes the collection of hardware resources host servers, rocks, enclosures,
storage and network hardware that makes up the datacenter infrastructure.
ii) Virtual Services offering
Workloads that are made up of the virtual machines, servers and or desktops that are
client facing and offer services.
5. Desktop Virtualization
Desktop virtualization has several advantages the least of which is the ability to centralize
desktop deployment and reduce distributed management costs because user’s access
centralized desktop through a variety of thin or unmanaged devices.
VMware Mobile Virtualization platform (MVP) is designed to create a virtual layer on
mobile handsets to allow you to run multiple mobile system on the same headset.
6. Presentation Virtualization
Present V until recently called Terminal Services, provide only the presentation layers
from a central locations to users, the protocols used for Present-V are at the forefront of
both Desk-V and Ser-V technologies since they are the protocols used to access, use
and manage virtual workloads.
7. Application Virtualization
AppV uses the same principal as software based. SerV but instead of providing an engine
to run an entire operating system, The application virtualization engine will make the virtualized
application run on any version of windows. What’s ever better is that products such as
Acress Software Admin Studio.
Admin studio both the citrix and the VMware Appv formats,major App-V vendors such
Server Virtualization Model:
There are two virtualization model for Ser-V are Hard-V and Soft-V
1. Soft-V Disadvantage:
It requires and underlying host OS
The underlying host OS also required resources
Soft-V should never be used in production.
2. Hard-V Disadvantage:
Hardware virtualization the hypervisor code will be integrated directly into the hardware.
If does not require patching and update.
Note: ESXi is 32 megabyte hypervisor that does not require an OS and can run directly from firmwar OS USB key.
The physical server running virtual machine workloads.
2. Guest Operating Systems (or) Virtual Machine (VM)
A virtualized operating system running as a workload on a host server.
Or
The underlying hypervisor software will run directly on the hardware and act as a coordinator to manage multiple operating system in VM.
3. Resource Pool
The collection of hardware resource, including host servers that make up datacenter infrastructure.
4. Virtual Service Offering
The virtual machine that are client facing and offer services to end users. They are also
often referred to as virtual workloads.
5. Virtual Appliances (VAPs)
Pre-packaged VSO’s that run a specific application or workload.
6. Policy based workloads.
VSO’s that are powered up on an as needed basis through automated policies.
7.Operating System virtualization
Often misconstrued as guest OS virtualization, this is nothing more than OS partitioning because it can only run one single OS type in parallel instances.
8. Hypervisor
A computer on which a hypervisor is running one or more virtual machines is defined as a host machine.
Two types of hypervisor:
i) Native type, (bare metal)
Hypervisors run directly on the host's hardware to control the hardware and to manage
guest operating systems.Modern equivalents of this are Oracle VM Server for SPARC, Oracle
VM Server for x86, the Citrix XenServer, VMware ESX/ESXi, KVM, and
Microsoft Core Hyper-V hypervisor.
Hypervisors run within a conventional operating system environment. VMware
Workstation, Microsoft Hyper-V and VirtualBox are examples of Type 2 hypervisors.
1. Citrix
Citrix offers a host of different virtualization technology.
Xen Server comes in four flavors
Express Edition
Standard Edition
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
Xen Desktop, Xen App
2. Microsoft
Virtual Server 2005 R2 SP1
Virtual PC 2007
Hyper-V
Terminal Services for Present V
Hyper-V 2012 Server
3. VMware
VMware Workstation
ESX Server hypervisor
VDI
Thin App
4. Oracle
Oracle VM
5. Novel
Xen
6. Red hat
Xen
7. IBM
Sun Virtual box
8. Virtual Iron.
Virtual Iron application





These are very useful Junior .
ReplyDeleteGo ahead and bring light into the world of knowledge.