Demo Firewall.
Demo Resource Allocation
OVF.
Virtual Switch
By default ESXi 5 virtual switch has two port group. old version has separate service console port group so three port group.
Command to see the vswitch and vmknic on troubleshooting mode.
# esxcfg-vswitch -l
# esxcfg-vmknic -l
Following images is old version and new version network port group.
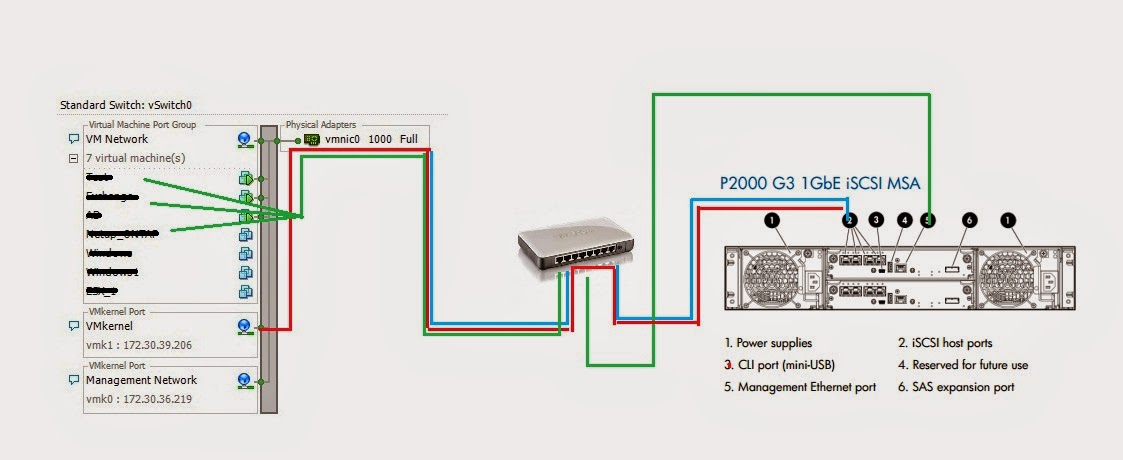
Storage
Show images from local system.
iSCSI
vCenter
Demo Resource Allocation
OVF.
- OVF stands for Open Virtual format
- OVF template contains one or more per-configured virtual machine that typically include a per-installed guest operating system and other software.
Virtual Switch
By default ESXi 5 virtual switch has two port group. old version has separate service console port group so three port group.
Command to see the vswitch and vmknic on troubleshooting mode.
# esxcfg-vswitch -l
# esxcfg-vmknic -l
Following images is old version and new version network port group.
Storage
Show images from local system.
iSCSI
- iSCSI is an acronym for Internet Small Computer System Interface
- Internet Protocol-based storage networking standard for linking data storage facilities
vCenter
- vCenter Server allows you to centrally manage multiple VMware ESX/ESXi host and virtual machine.
- vCenter server make ESXi host and vritual machine minimum downtime.
- or
- VMware vCenter is a service that act as a central administrator point for VMware vSphere host & connected on a network.
- One vCenter server connect upto 1000 host and 10,000 powered virtual machine.
- Two way to implement vCenter Server.
2. VCVA vCenter Server virtual appliance a linux based pre-configured guest operating system.
vCenter server advance features.
- Manual vMotion
- DRS (Distributed resource scheduler)
- HA (High Availability)
- FT (Fault Tolerance)
- Storage vMotion
- vCenter SSO
- vSphere web client server
- vCenter orchestrator
- VMware vSphere updated manager
- vCenter SRM (Site Recovery Manager)
Minium requirements for vCenter
- 64bit CPU
- 2GHZ
- 3GB of memory
- 3GB of disk space
- Supported OS win2003. 2003R2, 2008, 2008 R2.
- 4GB of memory upto 50 ESX/ESXI host and 500 powered on virtual machine.
- 4 CPU core & 8GB of memory for 300 ESX/ESXi host and 300 powered on virtual machine.
Database.
- SQL Server
- ORacle
- MYSQL
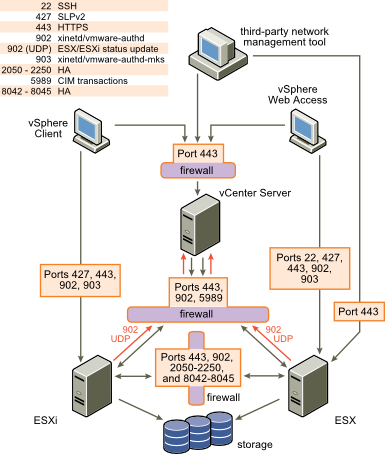
vSphere Client Communications with ESXi
vSphere Client Communications with vCenter
vSphere Network Configuration and Traffic Flow
Deploy vCenter & Demo Add ESX Host Demo.
Mount Storage to ESXi.
vCenter Server High availability.
- VMware vSphere® live migration allows you to move an entire running virtual machine from one physical server to another, without downtime.
- Transfer the virtual machine's active memory and precise execution state over a high-speed network, allowing the virtual machine to switch from running on the source vSphere host to the destination vSphere host. This entire process takes less than two seconds on a gigabit Ethernet network.
- High availability for vCenter Server is primarily implemented using vCenter server heartbeat and vSpher High Availability.
- HA heartbeat send the vmkernal port with managed HA and signnal to another esx hostHA agent or FDM (Fault domain management)
- Level of availabilityDowntime per year99%87 hours (3.5 days)99.9%8.76 hours99.99%52 minutes99.999%5 minutes
- EVC ensures that all hosts in a cluster present the same CPU feature set to virtual machines even if the actual CPUs on the hosts differ.
- Using EVC prevents migrations with vMotion from failing because of incompatible CPUs.
- EVC masks only those processor features that affect vMotion compatibility.
- Enabling EVC does not prevent a virtual machine from taking advantage of faster processor speeds, increased numbers of CPU cores, or hardware virtualization support that might be available on newer hosts.
First, it is reported by a master if the host responds to ICMP pings sent by the master over the management network but the FDM on the host cannot be reached by the master. This situation will occur if the FDM is unable to run or exit the uninitialized state- Second, it is reported by vCenter Server if it cannot connect to a master nor the FDM for the host. This situation would occur if all hosts in the cluster failed but vCenter Server is still running. It may also occur if all FDMs are unable to run or exit the uninitialized state
- The Fault Domain Manager on the host has been elected a master. This state is reported by the the host itself.
- ># Datastore
- ># MOID (Managed Object Identification number)
After election process VC give cluster into to master, master give to slave.
Heartbeat
- vCenter server heartbeat protects against planned and unplanned vCenter Server downtime. As an alternative, you can use vSphere HA for vCenter Server instances running on a virtual machine.
- vSphere HA protects against hardware and operating system failures.
- The vSphere High Availability (HA) feature for ESXi hosts in a cluster provides protection for a guest OS and applications running in a virtual machine by restarting the virtual machine if a guest OS or application failure occurs.
- The HA feature provides this reset capability through two different mechanisms:
- 1. Guest OS heartbeat issued by the VMware Tools process, known as VM Monitoring.
- 2.Heartbeat issued by a program that uses the HA Application Monitoring SDK to communicate with the VMware Tools process and the vSphere HA agent, known as Application Monitoring. This mechanism involves local monitoring by the program, thus avoiding the overhead of sending messages to and from vCenter Server.
- Using the HA Application Monitoring SDK, developers can write application monitoring programs in the C or C++ language.
- The application monitoring program sends an enable request to start the monitoring, followed by a heartbeat signal. The vSphere infrastructure passes the signal up from your HA application monitoring program to the virtual machine, and then to the ESXi host.
- The HA monitoring agent will reset the virtual machine if the application monitoring program stops sending a heartbeat signal.

Demo HA.
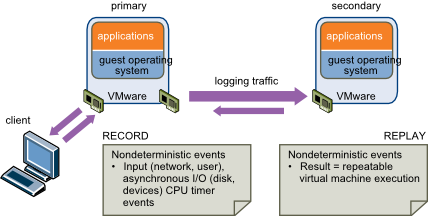
Falut Tolerance (FT)
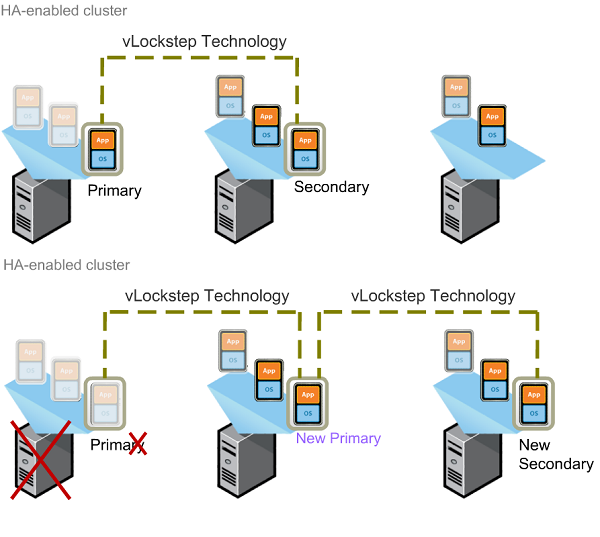
- You can enable VMware Fault Tolerance for your virtual machines to ensure business continuity with higher levels of availability and data protection than is offered by VMware HA.
- VMware Fault Tolerance provides continuous availability for virtual machines by creating and maintaining a Secondary VM that is identical to, and continuously available to replace, the Primary VM in the event of a failover situation.
- The Primary and Secondary VMs continuously exchange heartbeats. This exchange allows the virtual machine pair to monitor the status of one another to ensure that Fault Tolerance is continually maintained.
- A transparent failover occurs if the host running the Primary VM fails, in which case the Secondary VM is immediately activated to replace the Primary VM. A new Secondary VM is started and Fault Tolerance redundancy is reestablished within a few seconds. If the host running the Secondary VM fails, it is also immediately replaced. In either case, users experience no interruption in service and no loss of data.
- A fault tolerant virtual machine and its secondary copy are not allowed to run on the same host.
- Fault Tolerance is built on the ESX/ESXi host platform (using the VMware vLockstep technology), and it provides continuous availability by having identical virtual machines run in virtual lockstep on separate hosts
DRS (Distrubuted resource scheduler)
- VMware DRS (Distributed Resource Scheduler) is a utility that balances computing workloads with available resources in a virtualized environment.
- Feature that allocates and balances computing capacity dynamically across collections of hardware resources for virtual machines. This feature includes distributed power management (DPM) capabilities that enable a datacenter to significantly reduce its power consumption.
- Optimize power consumption dynamically within a vSphere cluster with VMware vSphere® Distributed Power Management™ (DPM), also included in vSphere Enterprise and Enterprise Plus editions.

SSO





No comments:
Post a Comment